In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, nitrogen oxides, collectively termed “NOx”, have emerged as one of the pivotal environmental concerns.
While their notorious impact on air quality and public health is widely acknowledged, the nuanced intricacies of NOx emissions often remain overshadowed.
This article delves deep into the origin of NOx emissions, placing it in a broader environmental context. Yet, our aim is not to perplex but to illuminate: we aim to unravel the multifaceted implications of NOx—beyond the headlines and into the lesser-discussed realms of its influence. Whether you're a seasoned researcher, an industry professional, or an inquisitive reader, journey with us as we simplify the complex, shedding light on the significant aspects of this crucial subject.
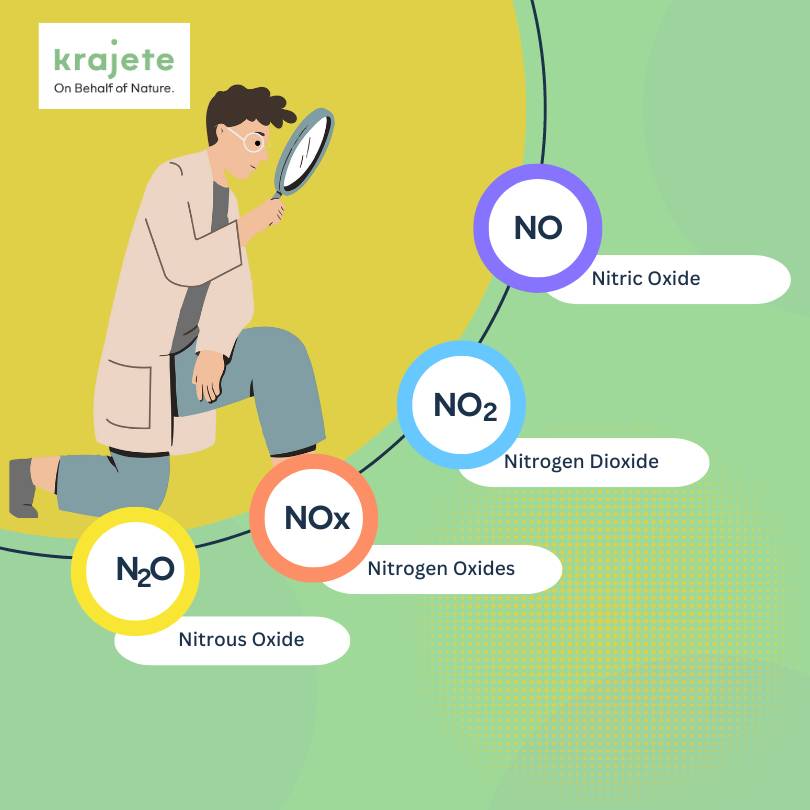
NOx, a shorthand notation used frequently in scientific circles, represents a family of highly reactive gases primarily composed of nitrogen and oxygen. These gases, chiefly nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO), play a pivotal role in atmospheric chemistry and have far-reaching impacts on both our natural surroundings and engineered environments.
Moving on to their origins, it's intriguing to note that not all NOx emissions stem from human activities. Nature has its own mechanisms for producing these compounds; lightning strikes and volcanic eruptions are prime examples. These natural sources, however, pale in comparison to the sheer volume introduced by human-made activities. Whether from vehicle exhausts, industrial processes, or the burning of fossil fuels, our modern world contributes significantly to the presence of these gases in our atmosphere. This distinction between natural and anthropogenic sources is pivotal when addressing mitigation strategies and understanding the broader implications of NOx emissions.
The landscape of human-generated NOx emissions is dominated by several significant contributors, each with its unique set of challenges and mitigation potentials.
Diving deeper into the science, the formation of NOx is an intricate dance of elements and conditions. At its core, the process results from combustion, particularly under high temperatures. During such events, the nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) naturally present in the air combine to form nitrogen oxides. The higher the temperature, the more favourable the conditions become for this combination to occur. This is especially evident in internal combustion engines and industrial furnaces, where the intense heat provides an ideal setting for NOx formation. Understanding this mechanism is vital, as it underscores the challenges faced in efforts to control and reduce these emissions.
Although invisible to the naked eye, NOx emissions have a tangible and profound effect on the air we breathe. They are precursors to two major environmental threats: smog and ground-level ozone.
NOx gases, while not the poster children for the greenhouse effect, possess a more insidious influence on our planet's warming. Directly, these gases aren't primary greenhouse culprits. However, as mentioned here above, they participate in a series of atmospheric reactions leading to the production of ozone.
This ozone, also called ground-level ozone or "Tropospheric ozone", acts as a potent greenhouse gas: Tropospheric ozone, a byproduct of NOx emissions, significantly affects evaporation, cloud formation, precipitation, and atmospheric circulation, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. Additionally, ozone in the troposphere harms human health and ecosystems and is a major smog component. Conversely, stratospheric ozone protects life by filtering ultraviolet radiation.
This indirect role of NOx—facilitating the creation of another potent greenhouse gas—accentuates the importance of managing and reducing its emissions.
NOx doesn't only act in isolation. When it intersects with pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the outcome is more than just additive – it is synergistic. Consider urban smog: It isn't solely the result of NOx or VOCs but emerges predominantly from their combined reactions under sunlight. This fusion leads to the creation of ground-level ozone. Similarly, in forested regions, the interplay between NOx and terpenes (a type of VOC released by trees) can result in amplified particle formation, affecting air quality and forest health. Such interactive effects highlight the intricate web of pollution challenges we face and the need for holistic solutions.
The cascade of environmental consequences from NOx emissions doesn't stop at air quality deterioration. Another alarming byproduct is acid rain. When NOx emissions ascend into the atmosphere, they readily react with atmospheric moisture to form nitric acid, which then precipitates as acid rain. This phenomenon isn't just a scientific curiosity; it has tangible repercussions like soil degradation: acid rain can severely alter the pH balance of soils, making it harder for vegetation to obtain the nutrients they require. Prolonged exposure to acid rain can deplete essential minerals in the ground, impairing plant health and causing severe damage to ecosystems.
Acid rain can also lead to water source contamination: Lakes, rivers, and streams aren't spared as acid rain leads to an accumulation of acidic compounds in these water bodies, endangering aquatic life. The Impact on aquatic ecosystems can be huge: These are vital reservoirs of biodiversity and are under threat from acid rain's influence :
But that is not the only way in which NOx emissions can impact aquatic biodiversity, as it plays a pivotal role in the ecological imbalance known as eutrophication, a process that significantly alters aquatic environments: When these nitrogen compounds from NOx deposits enter water bodies, they act as fertilisers, fueling an excessive growth of algae.
While these algal blooms might seem benign at first, they have cascading effects. As the algae die and decompose, they consume vast amounts of oxygen, creating "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot thrive. Fish and other marine species either perish due to this oxygen depletion or are forced to migrate to more hospitable areas. This phenomenon, recognised by organisations such as the Environmental Protection Agency, highlights once more the interconnectedness of air emissions and the health of our water systems.
NOx emissions' threats extend directly to human health, manifesting in various concerning ways:
Beyond its more direct impacts, NOx also plays a role in reducing clarity in our atmosphere. This diminished visibility isn't just an aesthetic concern; it can have practical implications for transportation and outdoor activities. The haze caused by the interplay of NOx and other airborne particles scatters sunlight, casting a pall over cityscapes and natural landmarks alike, altering our visual experience of the world around us.
The ripple effects of NOx emissions touch not only our environment but our economies as well. Hidden beneath the health advisories and smog warnings is a costly narrative. Hospitals see an uptick in admissions due to respiratory conditions, putting strain on healthcare systems. In our countryside, the spectre of acid rain, born from NOx, degrades soil and reduces agricultural yield – a double hit for farmers who bear the brunt of declining crop health and diminished market value. And consider tourism: pristine landscapes, once magnets for visitors, may lose their allure when haze reduces visibility or when areas of natural beauty show the scars of pollution.
This isn't merely about nature; it's a balance sheet concern that local and international economies need to grapple with.
As the challenges mount, so do the efforts to combat them. Regulatory measures have been sharpened, enforcing stricter NOx emission limits on industries and vehicles. Technological advancements, too, are making waves. From catalytic converters in automobiles to selective catalytic reduction systems in power plants, tools are in place that neutralise a significant portion of NOx before they even enter our atmosphere. Such interventions are more than just compliance; they're a testament to our collective endeavour to restore the delicate equilibrium of our environment.

The march of technology is relentless, and in the fight against NOx emissions, this is our ace card. Research labs and startups are buzzing with innovations: novel adsorbents that trap NOx more efficiently, biotechnologies harnessing microorganisms to neutralise pollutants, and even AI-driven monitoring systems optimising emission controls in real-time.
Each breakthrough, whether incremental or revolutionary, brings hope. The investments today in research, development, and scaling these innovations will dictate tomorrow's air quality.
This is why, at Krajete, we have embraced a dual mission: to shield our planet from the harmful effects of NOx and to ensure businesses thrive in the process.
By engineering cost-effective solutions, we're not just battling emissions but are also creating avenues for industries to flourish without compromising their bottom line.
We invite partnerships, collaborations, and dialogues at this crossroads of innovation and responsibility; Because together, we can rewrite the narrative of NOx, turning challenges into opportunities for a sustainable future.